Illustration (click to hide):
Project Description
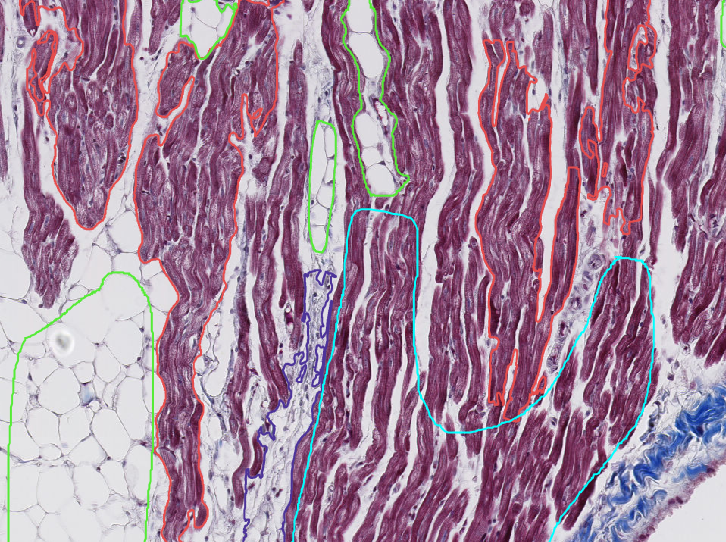
Histopathology will be employed to characterize cardiac tissue samples collected from dogs affected by Myxomatous Mitral Valve Disease (MMVD) or Dilated Cardiomyopathy (DCM) to increase knowledge about the cardiac remodeling process in cardiac diseased dogs. Artificial intelligence-based methods will be used in the image analysis process.
Samples were collected from seven anatomical locations in the hearts of eighty dogs, including the left ventricular anterior papillary muscle, left ventricular lateral wall, left ventricular posterior papillary muscle, septum, right ventricular lateral wall, right atrium, and left atrium. These samples were obtained from both control dogs and dogs with MMVD and DCM. A decision of euthanasia had been taken by the dog owners for reasons unrelated to the present study and tissue sampling was performed after the owner consented to sampling.
Masson’s trichrome staining technique was employed, as it can effectively demonstrate cardiomyocytes, adipose tissue, and connective tissue. All stained slides will now be analyzed using the image analysis software “QuPath” to characterize cardiomyocytes, adipocytes, fibrosis, and vessels in the various sample locations. The percentages of the area occupied by these structures will be compared between different diseases and disease severities to study the cardiac remodeling process of these heart diseases.
Project Information
-
BIIF Principal Investigators
- Christophe Avenel
External Authors
Sorawit Phetariyawong, Ingrid Ljungvall, -
Date
2024-02-06 🠚 Current