Illustration (click to hide):
Project Description
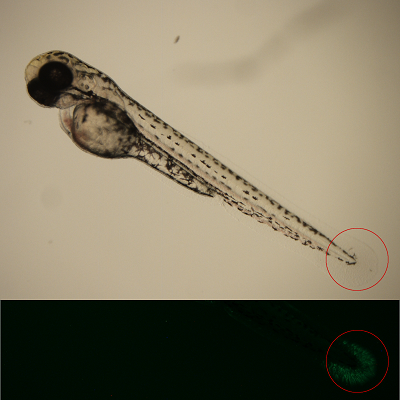
Wnt/beta-catenin signaling is involved in proliferation and fate of cells thus playing fundamental roles during embryo development. The specific aims of this part of the EU project are to 1) develop methods for detection of chemically induced changes in Wnt/beta-catenin signaling and to 2) determine developmental effects of EDC mixtures on Wnt/beta-catenin signaling. EDC-induced changes in Wnt/beta-catenin signaling are visualized and studied by transgenic zebrafish carrying a beta-catenin signaling fluorescent reporter (Tcf/Lef-miniP: d2EGFP).
Publication
Smirnova A, Mentor A, Ranefall P, Bornehag CG, Brunström B, Mattsson A, Jönsson M. Increased apoptosis, reduced Wnt/β-catenin signaling, and altered tail development in zebrafish embryos exposed to a human-relevant chemical mixture. Chemosphere. 2021 Feb;264(Pt 1):128467. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.128467. Epub 2020 Sep 30. PMID: 33032226.
Tags: Microscopy, model organisms and tissues
Project Information
-
BIIF Principal Investigators
- Petter Ranefall
- Carolina Wählby
External Authors
Maria Jönsson - Dept of Organismal Biology, Environmental Toxicology, Uppsala University. -
Date
2016-09-02 🠚 2017-07-07